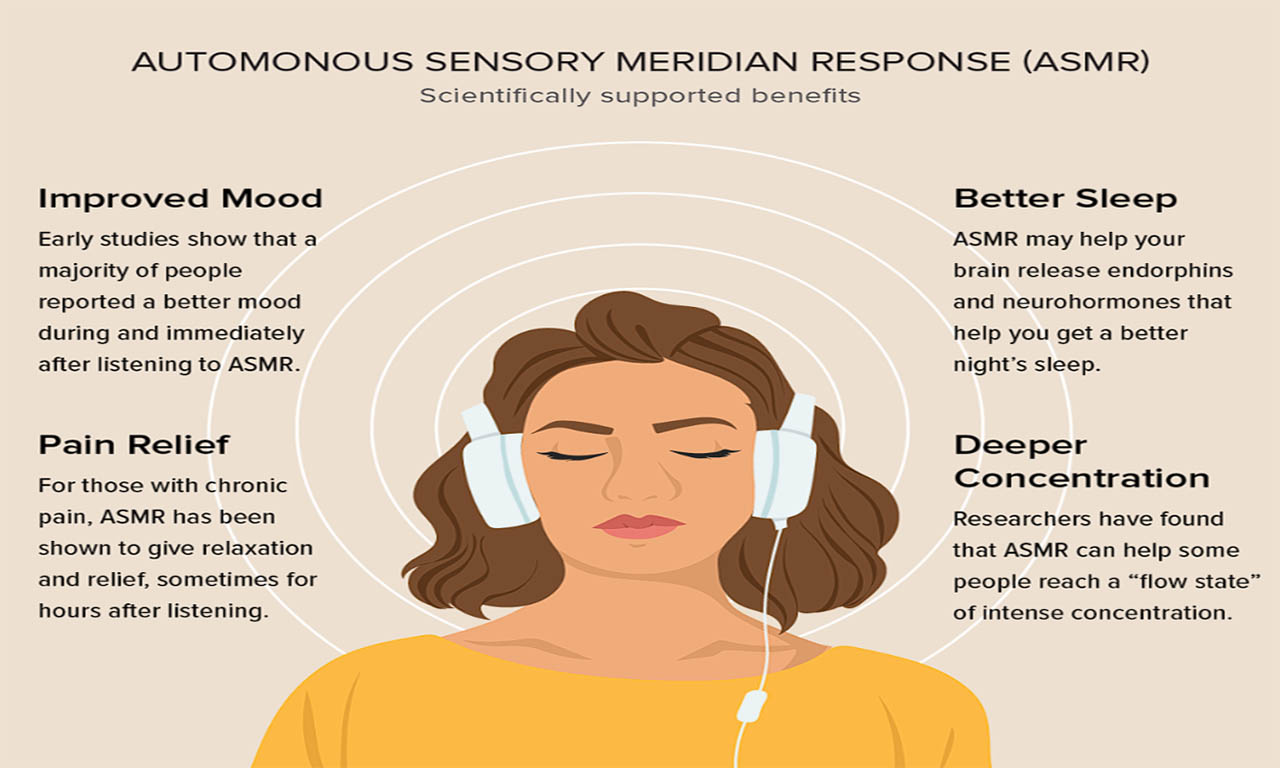
While ASMR has primarily been viewed through the lens of entertainment or relaxation, emerging research suggests potential medical applications:
Stress Reduction and Anxiety Management
One of the most prominent benefits of ASMR is its ability to induce relaxation and alleviate stress and anxiety. Studies have shown that ASMR triggers a significant reduction in heart rate and an increase in feelings of calmness and well-being. For individuals struggling with anxiety disorders or high-stress levels, ASMR videos or sessions could serve as a complementary relaxation technique.
Sleep Aid
Insomnia and sleep disturbances affect millions of people worldwide, contributing to various health issues. Preliminary research indicates that ASMR may offer benefits for improving sleep quality and duration. The calming effects of ASMR videos can help individuals unwind before bedtime, facilitating a smoother transition into sleep. Additionally, ASMR may reduce intrusive thoughts and promote a state of mental relaxation conducive to sleep.
Pain Management
While the mechanisms are not fully understood, some individuals report that ASMR can temporarily alleviate pain or discomfort. The gentle, soothing nature of ASMR triggers may distract individuals from physical discomfort, providing a brief reprieve from pain. Although ASMR is not a replacement for medical treatment, it could complement conventional pain management strategies and enhance overall well-being for those experiencing chronic pain conditions.
Mental Health Support
In the realm of mental health, ASMR has shown promise as a potential tool for managing symptoms of depression and loneliness. The personal attention and empathetic interactions depicted in ASMR videos may help individuals feel connected and understood, reducing feelings of social isolation. Moreover, the release of endorphins and oxytocin triggered by ASMR experiences could contribute to mood improvement and emotional regulation.
Understanding the Mechanisms
The precise mechanisms underlying ASMR remain an area of ongoing research. However, several theories have been proposed to explain its effects:
- Neurological Responses: Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies have revealed that ASMR triggers activate brain regions associated with emotional regulation, reward processing, and social cognition. These include the prefrontal cortex, insula, and anterior cingulate cortex, suggesting that ASMR may modulate emotional states and interpersonal experiences.
- Neurochemical Pathways: ASMR experiences are thought to involve the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin, which play key roles in mood regulation, bonding, and stress modulation. The release of these neurochemicals could contribute to the calming and pleasurable effects associated with ASMR.
- Sensory Stimulation: ASMR triggers often involve gentle tactile sensations and rhythmic auditory stimuli, which may activate specialized sensory pathways associated with pleasure and relaxation. The synchronized activation of sensory receptors could generate the characteristic tingling sensations and induce a state of heightened sensory awareness.
While ASMR continues to intrigue and captivate audiences worldwide, its medical potential offers a promising avenue for further exploration. From stress reduction and anxiety management to sleep improvement and pain alleviation, ASMR may offer a range of benefits for individuals seeking non-pharmacological interventions for various health concerns. As research in this field progresses, a deeper understanding of the physiological and psychological mechanisms underlying ASMR could unlock new opportunities for therapeutic applications and enhance overall well-being.